Introduction
Carports have become an increasingly popular alternative to full garages across the UK, offering affordable, flexible, and visually appealing protection for vehicles. These vehicle shelters can be attached to a home, positioned as a standalone structure, or designed for commercial use.

This guide explains the most common carport designs found across the UK, along with additional variations that homeowners and businesses often consider.
Carport Types
Free-standing Carport
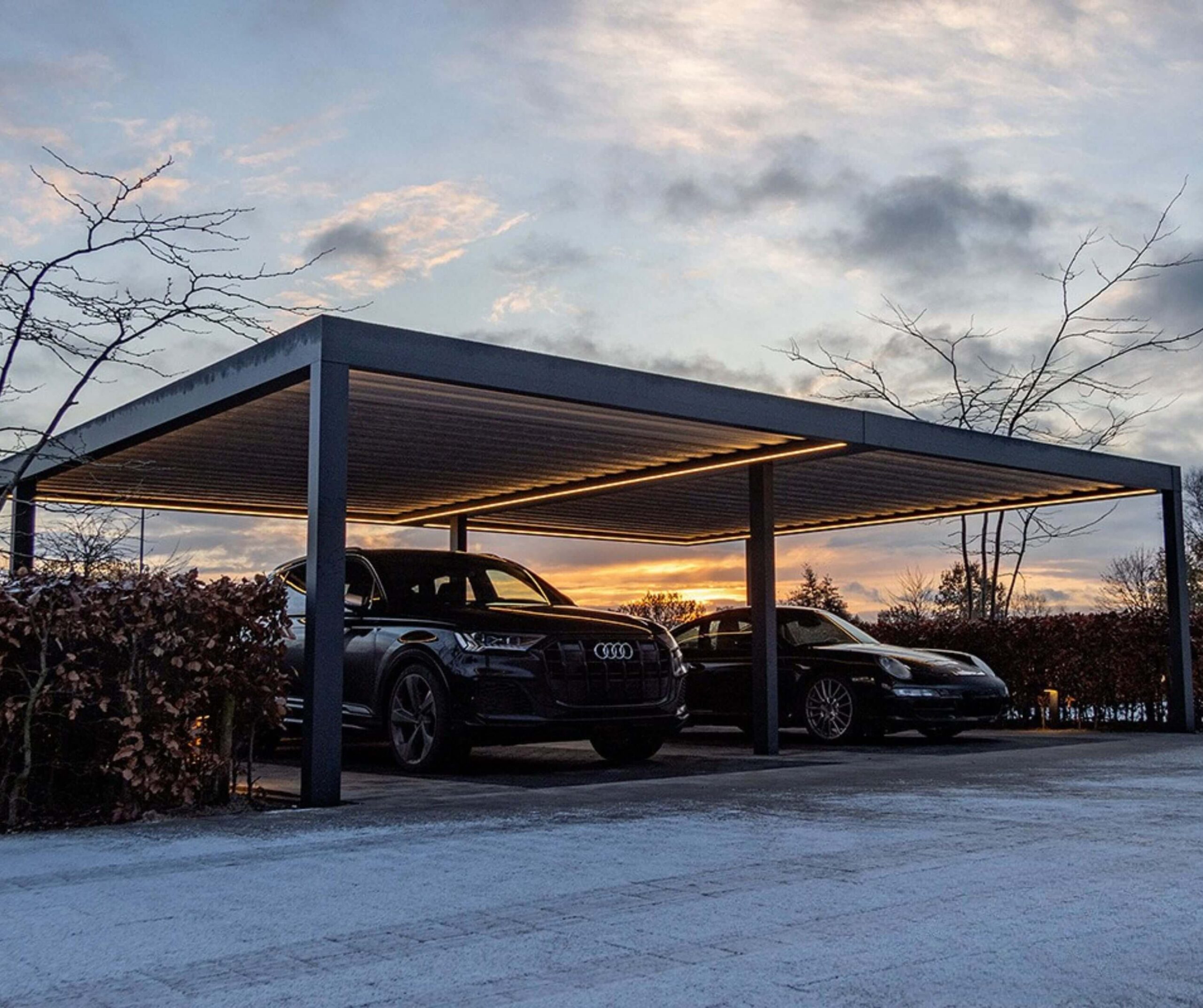
Free-standing carports are independent structures that do not rely on an existing building for support. They are ideal for properties with open space or when the carport needs to be positioned away from the home, for example, near a driveway entrance or on commercial sites.
Lean-to Carport
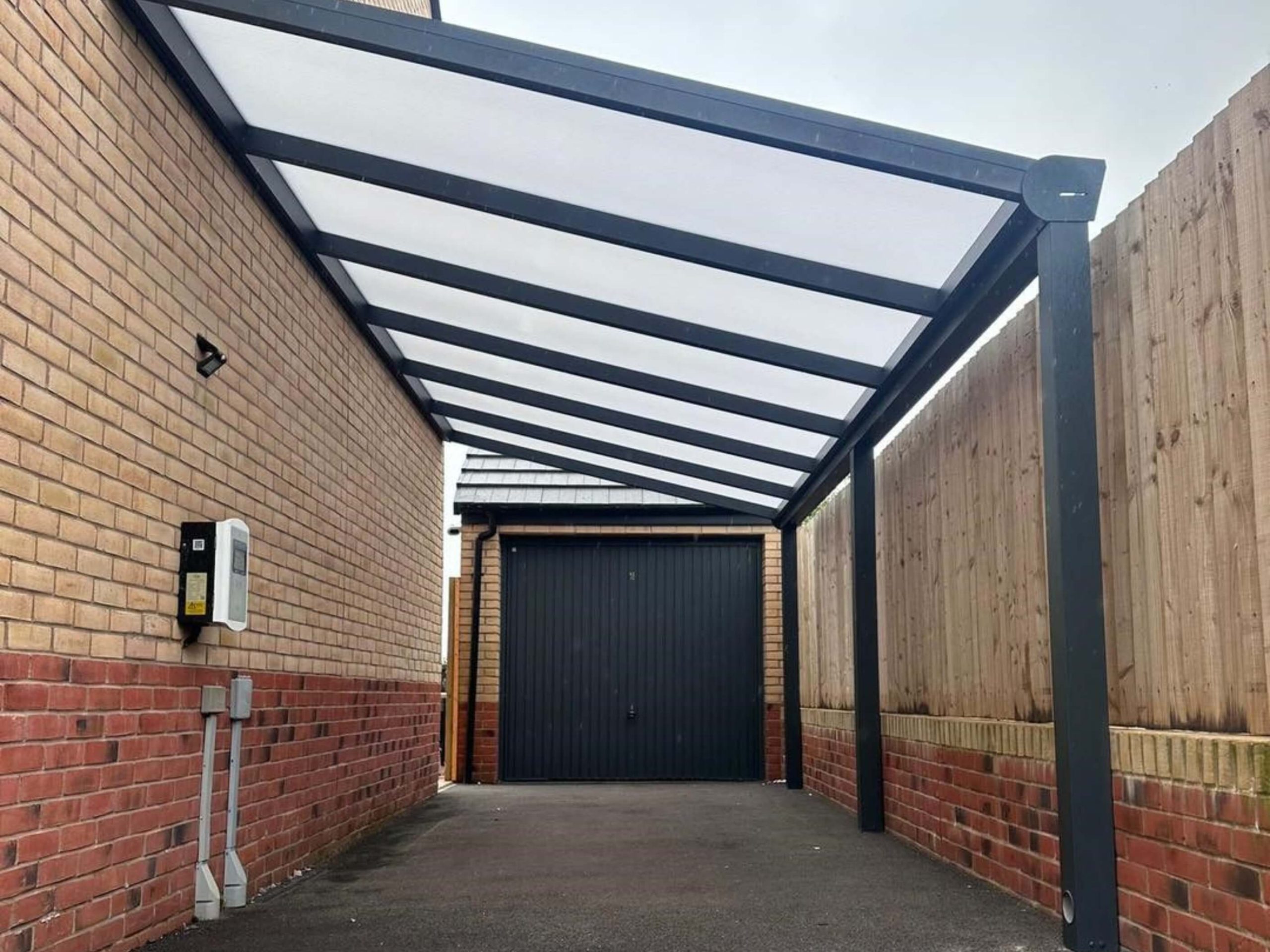
Lean-to carports attach directly to a house or outbuilding. They are particularly popular in the UK where driveway space is often limited. This type acts as a seamless extension of existing architecture and is ideal for narrow driveways or side-of-house parking.
Carport Designs
Single Carport
Single carports are designed to shelter one vehicle, making them a compact and cost-effective solution for one-car households in the UK. Despite being a single-vehicle solution, the layout can feel constrained when used with larger models.
Double Carport
Double carports can accommodate two vehicles side by side, which makes them a practical choice for larger households. However, the wider span requires more structural support, which therefore increases the cost of building one.
Commercial Carport
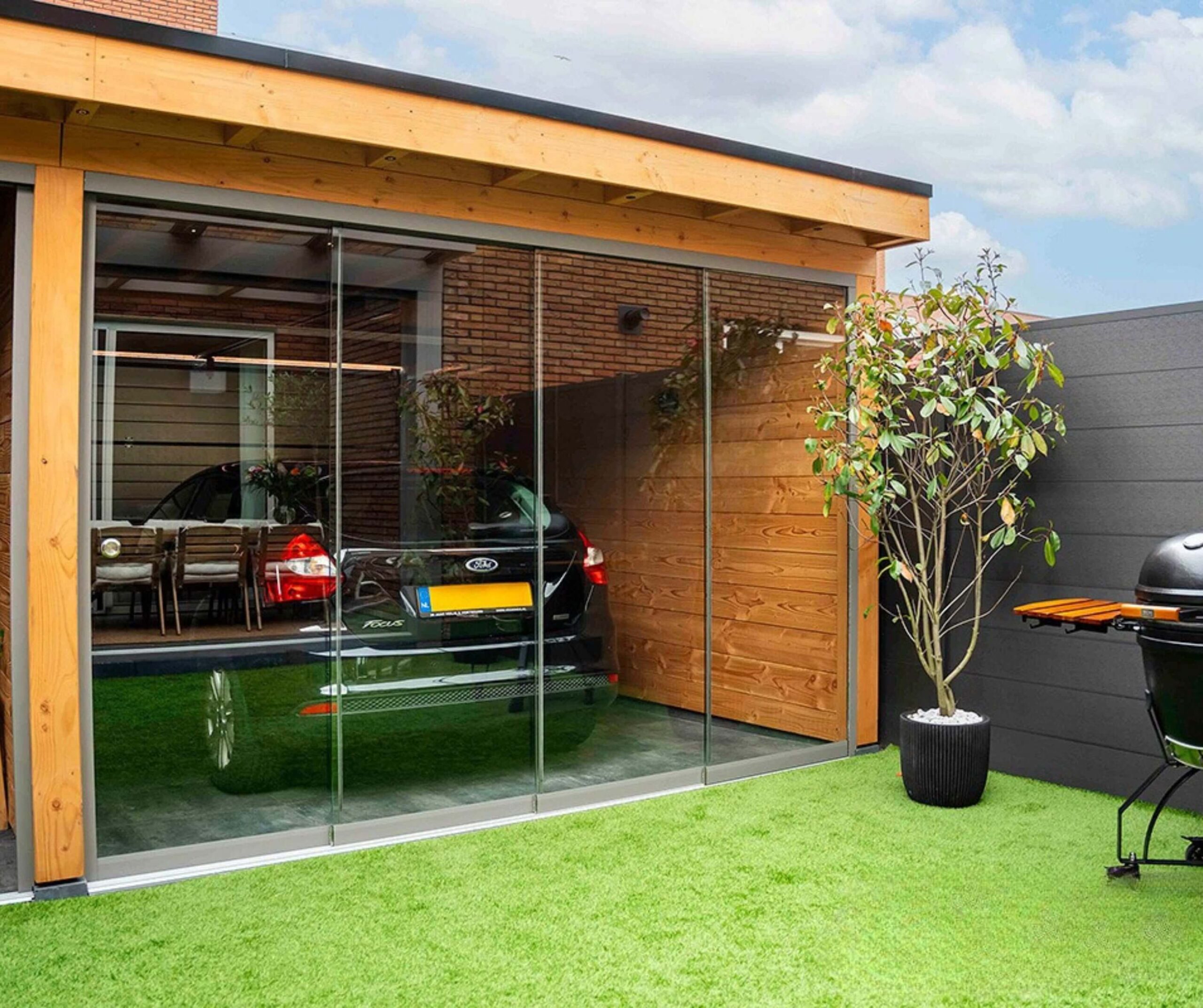
Commercial carports are increasingly used by institutional facilities and private businesses, to accommodate a fleet of vehicles, or provide sheltered parking for staff members and guests. Common applications include retail parks, office buildings, warehouses, residential complexes, car dealerships and public sector facilities. It is important to note that planning and installation for this design is more complex because the footprint, drainage requirements, and wind-load calculations are significantly higher than that of domestic carports.
Carport Roof Configurations
Flat Roof
Flat roofs are a common choice for free-standing and commercial carports, and often a practical solution for height-restricted spaces. However, drainage efficiency can be weaker than pitched designs, hence this configuration may require more ongoing maintenance to clear debris and standing water from the roof.
Pitched Roof
Pitched roofs are commonly used for lean-to carport installations, especially in residential settings. Their angled design encourages efficient water runoff, reducing both maintenance needs and debris build-up compared with flat roofs.
Carport Roof Materials
Toughened Glass Roof
Although heavier than alternative roofing materials, toughened glass gives the carport a high-end, architectural finish. However, opting for laminated or UV-coated glass is recommended, as this offers significantly better protection against UV exposure on bright, sunny days.
Polycarbonate Roof
This may not always provide the premium look and finish like a glass roof does but it is one of the most popular choices for domestic and commercial use, as it is more affordable, yet provides a strong UV-protection for vehicles sheltered underneath.
Conclusion
Each carport design has a clear purpose and a specific set of benefits and limitations. The most suitable option depends on property layout, local weather patterns, budget, and the level of convenience required.

By understanding the primary structures, roof types, and design variations, it can help you confidently select a carport that suits both functional needs and visual appeal.
Got a Question?
Got a question about carport designs, roofing choices, or technical details? Send us a message via the form below and we will assist you.
In the meantime, you can also browse the commonly asked questions below for quick answers.
Commonly Asked Questions
Protection against ultraviolet rays that cause fading, ageing and sun damage to the body and paint of vehicles.
Yes, when properly installed and rated for local wind loads, they are designed to withstand strong winds.
A strong, lightweight thermoplastic made from polycarbonate polymer resin. This impact-resistant material is widely used for roofing and glazing.